How To Read X Rays Of Knee
This x-ray clearly shows arthritis in the knee. Femur tibia fibula and patella.
 Total Knee Replacement Orthoinfo Aaos Knee Replacement Surgery Total Knee Replacement Hip Problems
Total Knee Replacement Orthoinfo Aaos Knee Replacement Surgery Total Knee Replacement Hip Problems
Check for patella tendon disruption.

How to read x rays of knee. Dont call a bipartite patella a fracture. One lateral knee view then will be exposed in the usual mediolateral projection while the other lateral may be taken lateromedially. This X-ray shows a healthy joint with nice sharp well-defined edges at the joint margins.
Well-corticated unfused center at the superolateral pole. Systematic reading of x-rays Information found on the x-ray are. Inferior pole of patella to tibial tuberosity.
The patella or kneecap is seen sitting in front and to the left of the femur. Remember that the knees of younger. This view clearly shows the four knee bones.
Especially in telling if you have arthritis or not. How to interpret postoperative X-rays after total knee arthroplasty Orthop Surg. This cartilage does not show up on x-ray so the bones should appear as though they are not.
It is easy to miss a fracture with only one view see red circle. Patella tendon length patella length 20. If possible slightly bend the knee in order to open the joint space.
Read A Knee X-Ray. Name and date of birth of the patient Side of extremitybody Date of x-ray Two views help to fully describe the fracture in both planes. If increased think patella tendon rupture.
A systematic approach involves checking alignment of bone structures joint spacing integrity of. Although the system for viewing X-rays of bones and joints varies depending on the anatomy being examined there are some broad principles which can be applied in a number of situations. Reading a knee x-ray is mostly easy.
Compare with your other knee. Soft tissue density in between the two fat pads. According to the study around 10 male and 13 female over the age of 60 are diagnosed with knee osteoarthritisWe can see how the knee of the patients suffering from arthritis is different from the knee of a normal person.
Knee X-rays 1. Know your knee anatomy. X-rays are best at showing bone but there is much more besides bone that can be seen on an X-ray.
Affiliation 1 All India Institute of Medical. Look for an effusion. The central ray is typically aimed 5-8 degrees cephalad and centered to the knee joint 15-20 cm distal to the apex of the patella.
School of Medicine Health Sciences University of North. Look for the distance between the femur and tibia on both the inside and outside. Typically for example when portable views of the knees are taken both lateral views may be exposed with the X-ray tube on the same side of the bed using a horizontal beam and elevating the knee to be examined.
See the the anatomical landmarks on the diagrams below. Authors Nishikant Kumar 1 Chandrashekhar Yadav Rishi Raj Sumit Anand. Your doctor will look for the following on your knee X-rays.
Our joints are covered with a layer of super-smooth cartilage that allows the joints to move without causing pain. Bones appear white on an x ray as they stop the x ray beam. A lateral view X-ray shows the knee from the side.
TRAUMA HORIZONTAL BEAM LATERAL TIPS. Make sure they are next to each other. Anything that lets the beam through air cartilage skin shows up as black.
They can also show signs of soft-tissue swelling and excess fluid within the knee. There are some things better to be left to a trained radiologist. Fractures are usually easy to spot.
However for the most part it is not too hard. This angulation allows the femoral epicondyles to superimpose vertically. The above image is the X-Ray image of knee arthritis which is a very common form of osteoarthritis among the older groups of people.
 Normal Anatomy Radiology Student Medical Radiography Radiology Tech
Normal Anatomy Radiology Student Medical Radiography Radiology Tech
 Radiographic Anatomy Femur Ap Radiology Student Diagnostic Imaging Anatomy
Radiographic Anatomy Femur Ap Radiology Student Diagnostic Imaging Anatomy
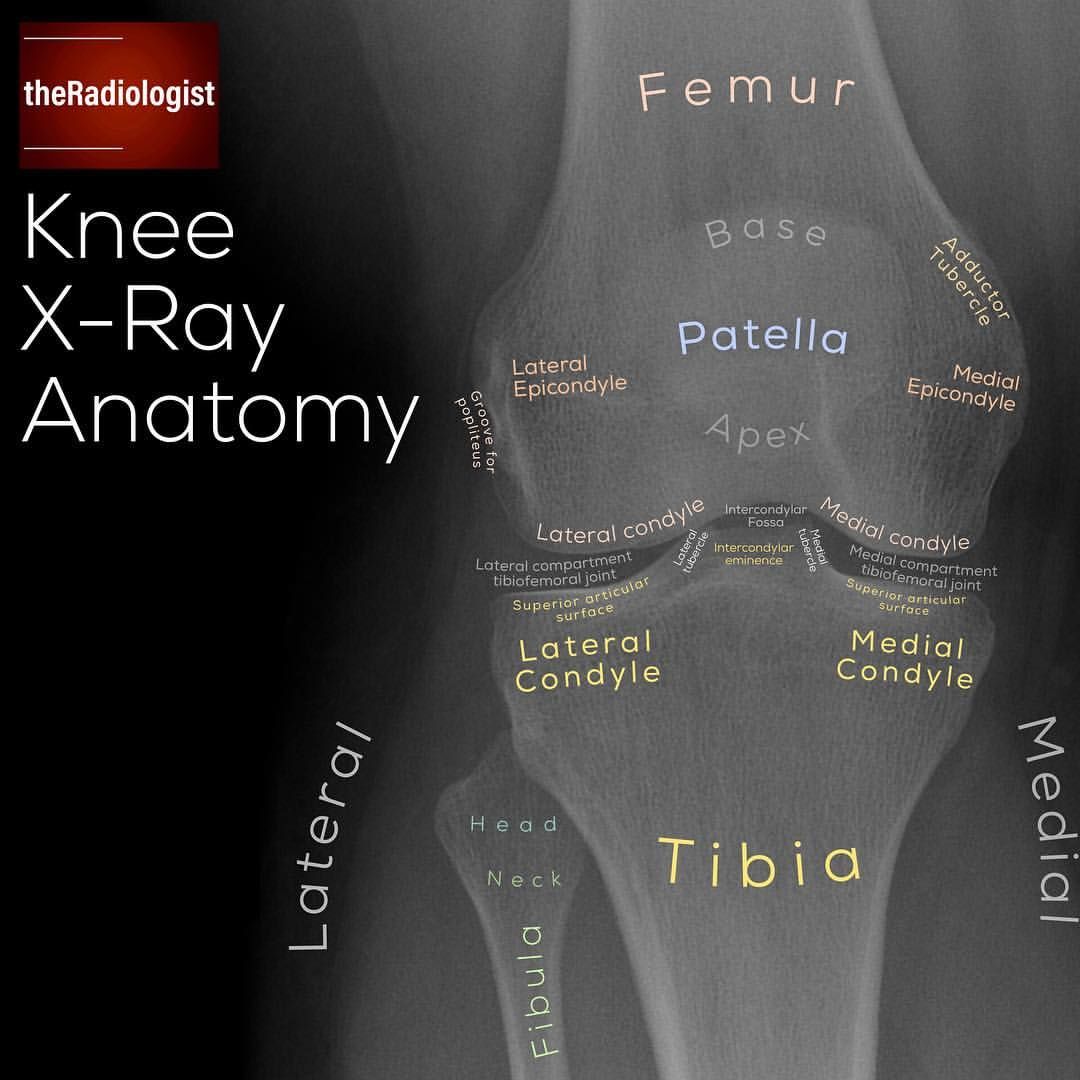 Read On For A System I Use When Looking At An Ap Knee X Ray The Ap Knee X Ray As Always No A Medical Knowledge Radiology Student Medical Technology
Read On For A System I Use When Looking At An Ap Knee X Ray The Ap Knee X Ray As Always No A Medical Knowledge Radiology Student Medical Technology
 5 145 Likes 82 Comments The Radiologist Theradiologistpage On Instagram Want To Learn A Syst Radiology Student Radiology Imaging Medical Anatomy
5 145 Likes 82 Comments The Radiologist Theradiologistpage On Instagram Want To Learn A Syst Radiology Student Radiology Imaging Medical Anatomy
 Normal Radiographic Anatomy Of The Knee 2 Distal Femoral Metaphysis 3 Patella 6 Medial Condyle 8 Lateral Cond Anatomy Of The Knee Radiology Anatomy
Normal Radiographic Anatomy Of The Knee 2 Distal Femoral Metaphysis 3 Patella 6 Medial Condyle 8 Lateral Cond Anatomy Of The Knee Radiology Anatomy
 Image Result For Over Rotated Knee X Ray Images Radiology Imaging X Ray X Ray Images
Image Result For Over Rotated Knee X Ray Images Radiology Imaging X Ray X Ray Images
 Take A Look At This Annotated X Ray Which Exhibits You The Place A Number Of The Pelvic Musc Medical Anatomy Radiology Student Radiology
Take A Look At This Annotated X Ray Which Exhibits You The Place A Number Of The Pelvic Musc Medical Anatomy Radiology Student Radiology
 Anterior Shoulder Dislocation General Review Radiology Student Radiology Basic Anatomy And Physiology
Anterior Shoulder Dislocation General Review Radiology Student Radiology Basic Anatomy And Physiology
 Hairline Fracture Ankle X Ray Hairline Fracture Hairline Fracture
Hairline Fracture Ankle X Ray Hairline Fracture Hairline Fracture
 Radiological Atlas Of The Lower Limb Radiograph Of The Knee Lateral View Showing Joints Femoropatellar Joint Radiology Student Radiology Imaging Radiology
Radiological Atlas Of The Lower Limb Radiograph Of The Knee Lateral View Showing Joints Femoropatellar Joint Radiology Student Radiology Imaging Radiology
 X Ray Of Arthritis In The Knee Compared To A Normal Knee Joint Note The Loss Of Joint Space Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Knee Arthritis Knee Osteoarthritis
X Ray Of Arthritis In The Knee Compared To A Normal Knee Joint Note The Loss Of Joint Space Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Knee Arthritis Knee Osteoarthritis
 Mri Knee Anatomy Knee Sagittal Anatomy Free Cross Sectional Anatomy Knee Mri Mri Anatomy
Mri Knee Anatomy Knee Sagittal Anatomy Free Cross Sectional Anatomy Knee Mri Mri Anatomy
 Read On For A Strategy I Use For Assessing A Horizontal Beam Lateral Hbl View Of The Knee Radiology Student Medical Knowledge Radiology Schools
Read On For A Strategy I Use For Assessing A Horizontal Beam Lateral Hbl View Of The Knee Radiology Student Medical Knowledge Radiology Schools
 X Rays Of Degenerative Left And Normal Right Knees Arthritis Loss Of Space Between Joints And That Causes Friction An Weak Bones X Ray Down On The Farm
X Rays Of Degenerative Left And Normal Right Knees Arthritis Loss Of Space Between Joints And That Causes Friction An Weak Bones X Ray Down On The Farm
 Tib Fib Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography Radiology Student Medical Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology
Tib Fib Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography Radiology Student Medical Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology



